Learn how COP I and COP II vesicle formed in diagram in step by step.
Abstract: It is very interesting to know how COP I & COP II vesicles formed when Retrograde and Anterograde transport occur.... Today we will highlight on the mentioned matter.
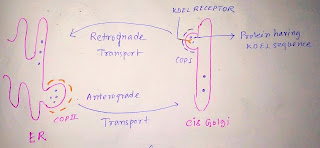
#An imaginary picture of anterograde and retrograde.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum resident protein has KDEL sequence at the protein c terminal end .
- KDEL receptor present in Golgi.
- KDEL receptor recognise ER resident protein and transport the protein to ER (Retrograde transport) by COP I .
ER transport their protein by vesicular transport by using COP II to Golgi.
Formation of COP I coated vesicle:
1.Recruitment of Sec7 (GEF) .
2. After recruitment of ARF1 from cytosol, Sec7 converts GDP to GTP of ARF1 and make it active from inactive form.
3.Hydrophobic tail present in ARF1 GTP which inserted into golgi membrane.
4.Finally COP I is activated by ARF1 .
5.As the picture before fusion the vesicle COP I to ER membrane, activated ARF1 will hydrolysis and convert itself GTP toGDP again.
6.Next COP I will dissociate and the vesicle simply fuse with ER membrane by the help of Rab effector , v-SNARE and t-SNARE (SEARCH IN MY WEBSITE TO KNOW)
Formation of COP II coated Vvesicle:
The process is quite same as COP I.
1.Here recruitment of Sec12 (GEF)
GEF: Guanine nucleotide Exchange Factor
It then activates Sar1(GDP to GTP)
2.Sar1 gives signal to COP II to which make vesicle formation .
3.sar 1 hydrolysis in GTP to GDP again.
4.COP II dissociate and fused with Golgi .
My website link: subhadipzoolover.blogspot. com
Thank you ...






Comments
Post a Comment